
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1/2 carat |
3/4 carat |
1 carat |
1 1/2 carat |
2 carat |
3 carat |
5 carat |
5.2 mm
.50 ct
50 points |
5.8 mm
.75 ct
75 points |
6.5 mm
1 ct
100 points |
7.4 mm
1.50 ct
150 points |
8.2 mm
2 ct
200 points |
9.4 mm
3 ct
300 points |
11.2mm
5 ct
500 points |
As with all precious stones, the weight - and therefore the size - of a diamond is expressed in carats. One carat is divided into 100 "points" so that a diamond of 25 points is described as a quarter of a carat, or 0.25 carats. Size is the most obvious factor in determining the value of a diamond, but now you know that two diamonds of equal size can have very unequal prices, depending on their quality. However, remember that diamonds of high quality can be found in all size ranges.
Due to their natural origins, total diamond weight may vary slightly for each piece. Learn about our allowable range.


 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| FL |
IF |
VVS1 |
VVS2 |
VS1 |
VS2 |
|
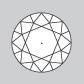
Flawless & Internally Flawless Diamonds have no inclusions visible under 10x magnification. |
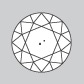
Very Very Slightly Included
Diamonds in the VVS grades have internal characteristics, but to such a slight degree that even a trained grader has a hard time finding them at 10x magnification. |
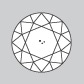
Very Slightly Included
Inclusions in stones in the VS category are more visible at 10x magnification than in VVS stones, but they are small or few in number. |
 |
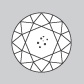 |
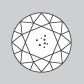 |
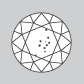 |
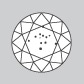 |
| SI1 |
SI2 |
I1 |
I2 |
I3 |
|
Slightly Included
Diamonds in the SI range have inclusions that are quite easy to see at 10x magnification, but usually invisible without magnification when viewed face up, through the table. |
Imperfect
These stones have inclusions that may be visible to the unaided eye and are very obvious under 10x magnification.
|


 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Colorless |
Near Colorless |
Faint Yellow |
Very Light Yellow |
Light Yellow |
| D |
E |
F |
|
|
G |
H |
I |
J |
|
K |
L |
M |
|
|
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
| |
|
|
|
X |
Y |
Z |
|
The most prized diamonds are colorless diamonds, because their beauty depends entirely upon their remarkable optical properties. In such diamonds, all the colors of the rainbow are reflected back to your eye. While the majority of gem diamonds appear to be colorless, others can contain increasing shades of yellow to brown, some of which are referred to as champagne diamonds. Other diamonds of exceptional color -- red, blue, green, pink and amber -- are known as "Fancies."
The color grading scale varies from totally colorless to light color or tinted. The difference between one grade.


 |
 |
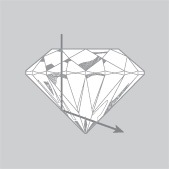 |
| Ideal Cut |
Shallow Cut |
Deep Cut |
Many people confuse cut with the shape of a diamond. The shape you select is a matter of individual taste, and today the skill and imagination of the craftsmen only limit your choice. It is their efforts during every stage of the fashioning process that reflects the maximum amount of light back to the eye. Most round brilliant cuts or fancy cuts such as cushion cut, princess cut and emerald cut possess 58 carefully angled flat surfaces, called facets. It is the precision of each facet's placement that will affect the amount of fire, brilliance and ultimate beauty of your Diamond.
When a diamond is cut to good proportions, light is reflected from one facet to another and then dispersed through the crown, or the top of the stone. If the cut of the diamond is too deep, some light escapes through the opposite side of the pavilion, or bottom. If the cut is too shallow, light escapes through the pavilion before it can be reflected.

